|
||
| Products Download Events Support Videos | ||
Technical Support
On-Line Manuals
µVision User's Guide
Arm C/C++ Compiler
Options dialog for ARM Compiler 5.
Preprocessor Symbols
- Define
-
Sets preprocessor symbols which can be checked with #if,
#ifdef and #ifndef. The defined names are copied
exactly as they are entered (case-sensitive). Optionally, each
name can get a value. For example,
is identical to the following C preprocessor #define statements: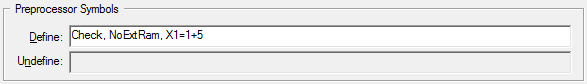
#define Check 1 #define NoExtRam 1 #define X1 1+5
Note
- Settings of the Define field get translated into the command line option -Doption.
-
To define X2 without setting a value, enter
-DX2=in the field Misc Controls.
- Undefine
- Clears previous Define assignments that are entered in the options dialog of a higher Target or Group level.
Language / Code Generation
- Enable ARM/Thumb Interworking
- Available only for CPUs that can switch between ARM and Thumb mode.
- Generates code that can be called in any CPU mode (ARM or Thumb). Sets the compiler command-line option --apcs=interwork.
- Execute-only Code
- Generates execute-only code and prevents the compiler from generating any data accesses to code sections. Creates code that does not have literal pools embedded in the code section, hence the HW can enforce that only the instruction fetch is allowed to read from the memory (protection of firmware).
-
Restricted to
- C code.
- Thumb code.
- Cortex-M3 and Cortex-M4 processor-based devices.
- armcc compiler version 5.04 and above.
The flag sets the compiler command-line option --execute_only. - Optimization
-
Control compiler code optimization for the generated code. Sets
the compiler command-line option -Onum:
- Default: Use the compiler default or the setting of a higher Target or Group level.
- Level 0 (-O0): Turn off all optimization, except some simple source transformations.
- Level 1 (-O1): Turn off optimizations that seriously degrade the debug view.
- Level 2 (-O2): High optimization (default level). The debug view might be less satisfactory because the mapping of object code to source code is not always clear.
- Level 3 (-O3): Maximum optimization. Note that Level 3 in combination with Optimize for Time may generate more code that Level 2 since it may unroll loops.
- Optimize for Time
- Reduce execution time at the possible expense of a larger code size. Sets the compiler command-line option -Otime. If not enabled, the compiler assumes -Ospace.
- Split Load and Store Multiple
- Instructs the compiler to split LDM and STM instructions into two or more LDM or STM instructions to reduce interrupt latency. When the LDM/STM have more than 5 (more than 4 when the PC is changed) CPU registers, several LDM/STM instructions are generated. Sets the compiler command-line option --split_ldm.
- One ELF Section per Function
- Generate one ELF section for each function in source file. Output sections are named with the same name as the function that generates the section. Allows you to optimize code or to locate each function on individual memory addresses. Sets the compiler command-line option --split_sections.
- Strict ANSI C
- Check for strict ANSI C conformance of the source file. Sets the compiler command-line option --strict.
- Enum Container always int
- When disabled, the data type container for enum is optimized according to the value range. When enabled, the data type container for enum is always signed int. Sets the compiler command-line option --enum_is_int. See also remarks in --interface_enums_are_32_bit.
- Plain Char is Signed
- Instructs the compiler to treat all variables declared with plain char as signed char. Sets the compiler command-line option --signed_chars.
- Read-Only Position Independent
- Generate position independent code for const (ROM) accesses. Sets the compiler command-line option --apcs=/ropi.
- Read-Write Position Independent
- Generate position independent code for variable (RAM) accesses. Sets the compiler command-line option --apcs=/rwpi.
- Warnings
- Control generation of warning messages. Default is unspecified, which defaults to All Warnings. The selection No Warnings sets the command-line option -W.
- Thumb Mode
- Select explicitly Thumb or ARM code for a file or file group. Note: in the dialog Target, the selection of the field Code Generation sets the default.
- No Auto Includes
- Suppress all C/C++ paths that are included automatically during compilation. System includes, such as stdio.h, are not affected by the settings of this box. Compiler auto-include paths can be viewed in the field Compiler control string.
- C99 Mode
-
The compiler compiles C as defined by the 1999 C standard and
addenda:
- ISO/IEC 9899:1999. The 1999 International Standard for C.
- ISO/IEC 9899:1999/Cor 2:2004. Technical Corrigendum 2.
-
- Include Paths
- Allows you to supply one or more (separated by semi-colon) paths to search for header files. For example, for #include "filename.h" the compiler searches the current folder first and then the folder of the source file. When this fails or when #include <filename.h> is used, the paths specified in the include paths box are searched. When this search fails again, then the paths specified in the field INC under Project — Manage — Project Items are used.
- Misc Controls
- Specify any directive for which there is no individual dialog control. For example, to change the error message language to Japanese refer to Show Japanese Messages.
- Compiler control string
- Displays the current directives at the compiler command line. Scroll down in the field to view all directives.
-
The following control strings are added, depending on the use of
MDK:
Control String Description __UVISION_VERSION Major and minor version of µVision. For example: -D__UVISION_VERSION="520"._RTE_ Set when RTE is in use. For example: -D_RTE_.__RTX Set when RTX Kernel has been selected in Options for Target - Target - Operation System. Not set when using RTE. For example: -D__RTX.__MICROLIB Set when Use MicroLIB has been enabled in Options for Target - Target. For example: -D__MICROLIB.__EVAL µVision runs in evaluation mode. License MDK-Lite. For example: -D__EVAL.device header name Device header name.
ProductsDevelopment Tools |
Hardware & Collateral |
Downloads |
Support |
Contact |
