|
||
| Products Download Events Support Videos | ||
Product Information
Device Database®
Downloads
Compliance Testing
Distributors
Peripheral Simulation
For Atmel AT91C140 — USART1
Simulation support for this peripheral or feature is comprised of:
- Dialog boxes which display and allow you to change peripheral configuration.
- VTREGs (Virtual Target Registers) which support I/O with the peripheral.
These simulation capabilities are described below.
USART 1 Dialog
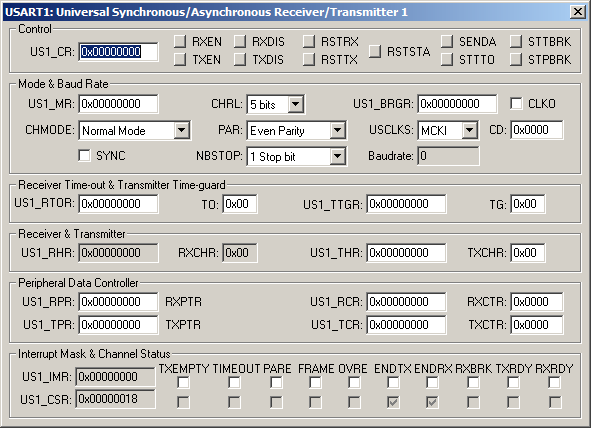
The USART 1 Dialog configures USART 1. A USART transfers serial data to and from external devices and the ARM controller. The USART can be configured in a variety of ways to suit the external serial device.
Control Group
- US1_CR (USART 1 Control Register) displays the combined control information for the following:
- RXEN (Receiver Enable) click to enable the receiver.
- TXEN (Transmitter Enable) click to enable the transmitter.
- RXDIS (Receiver Disable) click to disable the receiver.
- TXDIS (Transmitter Disable) click to disable the transmitter.
- RSTRX (Reset Receiver) click to reset the receiver.
- RSTTX (Reset Transmitter) click to reset the transmitter.
- RSTSTA (Reset Status Bits) click to reset the Parity Error (PARE), Framing Error (FRAME), Overrun Error (OVRE) and Break Received (RXBRK) status bits.
- SENDA (Send Address) click to set the address bit with the next character written (multi-drop mode only).
- STTTO (Start Time-out) click to restart the wait time-out for a new character.
- STTBRK (Start Break) click to generate a break condition after the next character is sent.
- STPBRK (Stop Break) click to cancel a break condition.
Mode & Baud Rate Group
- US1_MR (Mode Register) contains the USART Mode settings which is which is determined by settings of other controls in this group.
- CHMODE (Channel Mode) selects normal, loopback, echo or remote loopback pin configurations.
- SYNC (Synchronous Mode Select)
- CHRL (Character Length) selects the number of bits per character.
- PAR (Parity Type) selects the generation of even, odd or no parity bits, mark or space, or multi-drop mode.
- NBSTOP (Number of Stop Bits) selects the number of stop bits to be sent with each character.
- US1_BRGR (Baud Rate Generator Register) holds the Clock Divisor (CD) value.
- USCLKS (Clock Selection) selects clock source and type.
- Baudrate displays the baud rate calculated by the USART.
- CLKO (Clock Output Select)
- CD (Clock Divisor) contains the value divided into the clock that determines the baud rate.
Receiver Time-out & Transmitter Time-guard Group
- US1_RTOR (Receiver Time-out Register) holds the receiver time-out value.
- TO (Time Out) sets the time-out counter value used with the Start Time-out command.
- US1_TTGR (Transmitter Time-guard Register) holds the transmitter time guard value.
- TG (Time-guard) sets the length of time TXD is inactive after each character.
Receiver & Transmitter Group
- US1_RHR (Receiver Holding Register)
- RXCHR (Received Character) holds the last character received.
- US1_THR (Transmitter Holding Register)
- TXCHR (Character to be Transmitted) holds the next character to be transmitted.
Peripheral Data Controller Group
- US1_RPR (Receive Pointer Register) holds the receive buffer address.
- US1_TPR (Transmit Pointer Register) holds the transmit buffer address.
- US1_RCR (Receive Counter Register) holds the receive counter (RXCTR) value.
- US1_TCR (Transmit Counter Register) holds the transmit (TXCTR) value.
- RXCTR (Receive Counter) contains the size of the receive buffer.
- TXCTR (Transmit Counter) contians the size of the receive buffer.
Interrupt Mask & Channel Status Group
- US1_IMR (Interrupt Mask Register)
- US1_CSR (Channel Status Register)
- TXEMPTY (Transmitter Empty) set if there are no characters in the transmitter hold register(US1_THR).
- TIMEOUT (Receiver Time-out) set if a Start Time-out counter has elapsed.
- PARE (Parity Error) set if the controller detects at least 1 false parity bit since the last Reset Status Bits command (RSTSTA).
- FRAME (Framing Error) set if the controller detects a framing error since the last Reset Status Bits command (RSTSTA).
- OVRE (Overrun Error) set if the controller detects an overrun condition since the last Reset Status Bits command (RSTSTA).
- ENDTX (End of Transmitter Transfer) is set if the End of Transmitter signal is active.
- ENDRX (End of Receiver Transfer) is set if the End of Receiver signal is active.
- RXBRK (Break Received/End of Break) is set if the USART receives a break since the last Reset Status Bits command (RSTSTA).
- TXRDY (Transmitter Ready) set if the transmit hold register (US1_THR) is empty and there is no break request pending.
- RXRDY (Receiver Ready) set when the USART receives at least 1 character and the receiver hold register (US1_RHR) is not empty.
SxEXTCLK VTREG
Data Type: unsigned long
The SxEXTCLK VTREG contains the frequency of an External Clock input for Serial Port 0, 1, and so on.
SxIN VTREG
Data Type: unsigned int
The SxIN VTREG represents the serial input of the simulated microcontroller. Values you assign to SxIN are input to the serial channel 0, 1, 2, and so on. You may assign input using the command window. For example,
S0IN='A'
causes the simulated microcontroller serial input 0 to receive the ASCII character A. If you want to use the SxIN VRTEG to simulate reception of multiple characters, you must be sure to delay for at least one character time between successive assignments to SxIN. This may be done using a signal function. For example:
signal void send_cat (void) {
swatch(0.01); /* Wait 1/100 seconds */
S0IN='C'; /* Send a C */
swatch(0.01);
S0IN='A';
swatch(0.01);
S0IN='T';
}
You may use the SxIN VTREG to input data (5-9 bits), parity, frame error and break condition. SxIN Format (16-bit Register)
- Bits 0-8: Data (5, 6, 7, 8 or 9 bit)
- Bit 9: Parity bit Value
- Bit 10: Parity bit Presence (0=Not present, 1=Present)
- Bit 11: Invalid Stop bit (0=Normal, 1=Invalid)
- Bit 12: End of Break
For example:
S0IN=0x0074 // Data = 0x74, No Parity bit
S0IN=0x0174 // Data = 0x174, No Parity bit
S0IN=0x0474 // Data = 0x74, Parity bit = 0
S0IN=0x0674 // Data = 0x74, Parity bit = 1
S0IN=0x0874 // Data = 0x74, No Parity bit
// Invalid Stop bit - Frame Error
S0IN=0x0800 // Break Condintion
S0IN=0x1000 // End of Break Condition
In addition to the SxIN VRTEG, the serial window allows you to input serial characters by simply typing. Serial characters that are transmitted byt the simulated microcontroller appear in the serial window.
SxOUT VTREG
Data Type: unsigned int
The SxOUT VTREG represents the serial output from the simulated serial port 0, 1, and so on. Whenever the simulated serial port transmits a character, the value transmitted is automatically assigned to SxOUT (which is read-only). You may read the value of SxOUT to determine the character transmitted by your simulated program. For example,
S0OUT
outputs the value of the last character transmitted by serial port 0.
SxOUT Format (16-bit Register)
- Bits 0-8: Data (5, 6, 7, 8 or 9 bits)
- Bit 9: Parity bit Value
- Bit 10: Parity bit Presence (0=Not present, 1=Present)
- Bit 11: Invalid Stop bit (0=Normal, 1=Invalid)
- Bit 12: End of Break
For example:
S0OUT & 0x01FF // Data S0OUT & 0x0400 // Parity bit is present S0OUT & 0x0200 // Parity bit value (0=0, 0x0200=1)
Note that you cannot assign values to the SxOUT VTREGs. You may use the SxOUT VTREG in a script to process transmitted data. For example,
signal void s0out_sig (void) {
while (1)
{
wwatch(S0OUT); /* wait for something in S0OUT */
printf ("Transmitted a %2.2X\n", (unsigned) S0OUT);
}
}
SxTIME VTREG
Data Type: unsigned char
The SxTIME VTREG allows you to control the timing of the simulated serial port 0, 1, and so on.
- A value of 1 (which is the default) indicates that the serial port timing is identical to the target hardware. Use this value when you want to see the effects of baud rate on the serial port I/O.
- A value of 0 indicates that all serial input and output occur instantaneously. Use this value when you don't care about any baud rate effects or when you want serial output to be fast.
For example:
S0TIME = 0 /* Set Serial Port 0 for FAST timing */ S0TIME = 1 /* Set Serial Port 0 for accurate timing */
ProductsDevelopment Tools |
Hardware & Collateral |
Downloads |
Support |
Contact |
